The latest ceramic resistor specifications
The Latest Ceramic Resistor Specifications
I. Introduction
Ceramic resistors are a crucial component in the world of electronics, serving as essential elements in various circuits and devices. Defined as resistors made from ceramic materials, they are known for their stability, reliability, and ability to withstand high temperatures. As technology continues to advance, the specifications and capabilities of ceramic resistors have evolved, making them indispensable in modern electronic applications. This article aims to provide an overview of the latest specifications and advancements in ceramic resistors, highlighting their importance in various industries.
II. Overview of Ceramic Resistors
A. Composition and Structure
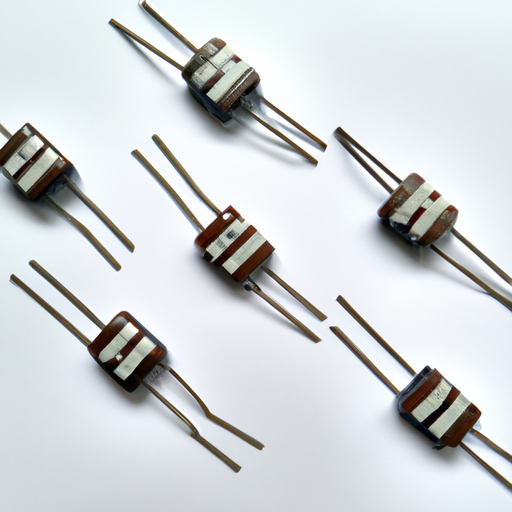
Ceramic resistors are primarily composed of ceramic substrates, which provide excellent thermal and electrical insulation. The materials used in their construction can vary, but they often include metal films or thick film pastes that are applied to the ceramic substrate.
1. **Materials Used**: Common materials include alumina (Al2O3) for the substrate and various metal oxides for the resistive layer. The choice of materials significantly influences the resistor's performance characteristics.
2. **Types of Ceramic Resistors**: There are two main types of ceramic resistors: thick film and thin film. Thick film resistors are made by printing a resistive paste onto the substrate, while thin film resistors are created by depositing a thin layer of resistive material through vacuum deposition techniques. Each type has its unique advantages and applications.
B. Working Principle
Ceramic resistors function by converting electrical energy into heat through resistive heating. When an electric current passes through the resistor, it encounters resistance, which generates heat.
1. **How Ceramic Resistors Function**: The resistive material's properties determine how much resistance is encountered, which in turn affects the current flow and voltage drop across the resistor.
2. **Comparison with Other Resistor Types**: Compared to carbon and metal film resistors, ceramic resistors offer superior thermal stability and can operate at higher temperatures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
III. Key Specifications of Ceramic Resistors
A. Resistance Values
Ceramic resistors are available in a wide range of resistance values, typically from a few ohms to several megaohms.
1. **Range of Resistance Values Available**: This versatility allows them to be used in various applications, from simple circuits to complex electronic systems.
2. **Tolerance Levels**: Tolerance levels for ceramic resistors can range from ±1% to ±5%, with some high-precision variants offering even tighter tolerances.
B. Power Rating
The power rating of a ceramic resistor indicates the maximum amount of power it can dissipate without failing.
1. **Definition and Importance**: Power ratings are crucial for ensuring that resistors can handle the electrical load in a circuit without overheating.
2. **Typical Power Ratings for Different Applications**: Common power ratings for ceramic resistors range from 0.1 watts to several watts, depending on the application requirements.
C. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient of a resistor indicates how its resistance changes with temperature.
1. **Explanation of Temperature Coefficient**: A low temperature coefficient means that the resistor's resistance remains stable across a range of temperatures, which is vital for precision applications.
2. **Impact on Performance and Reliability**: A stable temperature coefficient enhances the reliability of the resistor in varying environmental conditions, making ceramic resistors ideal for high-performance applications.
D. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating specifies the maximum voltage that can be applied across the resistor.
1. **Maximum Operating Voltage**: Exceeding this voltage can lead to breakdown and failure of the resistor.
2. **Importance in Circuit Design**: Understanding the voltage rating is essential for engineers to ensure that the resistor can safely operate within the circuit's voltage levels.
IV. Latest Advancements in Ceramic Resistor Technology
A. Enhanced Thermal Management
Recent advancements in ceramic resistor technology have focused on improving thermal management.
1. **New Materials and Coatings**: Innovations in materials science have led to the development of new ceramic compositions and coatings that enhance heat dissipation.
2. **Improved Heat Dissipation Techniques**: Techniques such as the use of heat sinks and advanced thermal interface materials are being employed to further improve thermal performance.
B. Miniaturization Trends
As electronic devices become smaller and more compact, the demand for miniaturized components has increased.
1. **Smaller Form Factors**: Manufacturers are producing ceramic resistors in smaller sizes without compromising performance, allowing for more efficient use of space in electronic designs.
2. **Implications for Modern Electronics**: This trend towards miniaturization is particularly important in consumer electronics, where space is at a premium.
C. Increased Precision and Stability
Advancements in manufacturing processes have led to increased precision and stability in ceramic resistors.
1. **Advances in Manufacturing Processes**: Techniques such as laser trimming and automated production lines have improved the consistency and quality of ceramic resistors.
2. **Impact on High-Performance Applications**: These improvements are particularly beneficial in high-performance applications, such as telecommunications and aerospace, where precision is critical.
V. Applications of Ceramic Resistors
A. Consumer Electronics
Ceramic resistors are widely used in consumer electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and other devices.
1. **Use in Smartphones, Laptops, and Other Devices**: Their reliability and stability make them ideal for applications where performance is crucial.
B. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, ceramic resistors play a vital role in various systems.
1. **Role in Electric Vehicles and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)**: They are used in power management systems and safety features, contributing to the overall performance and safety of vehicles.
C. Industrial Applications
Ceramic resistors are also prevalent in industrial applications.
1. **Use in Automation and Control Systems**: Their durability and reliability make them suitable for harsh industrial environments.
D. Medical Devices
In the medical field, ceramic resistors are essential components in diagnostic and therapeutic equipment.
1. **Importance in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Equipment**: Their precision and stability are critical for ensuring accurate measurements and safe operation in medical devices.
VI. Challenges and Considerations
A. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions can significantly impact the performance of ceramic resistors.
1. **Impact of Humidity and Temperature on Performance**: High humidity and extreme temperatures can affect the reliability and lifespan of ceramic resistors.
B. Reliability and Longevity
Ensuring the reliability and longevity of ceramic resistors is a key consideration for manufacturers and engineers.
1. **Factors Affecting Lifespan**: Factors such as thermal cycling, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure can influence the lifespan of ceramic resistors.
C. Cost Considerations
Balancing performance and cost is a critical challenge in the design and selection of ceramic resistors.
1. **Balancing Performance and Budget**: Engineers must consider the trade-offs between high-performance resistors and budget constraints when designing electronic systems.
VII. Future Trends in Ceramic Resistor Development
A. Research and Development Directions
The future of ceramic resistors is promising, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on innovation.
1. **Innovations in Materials Science**: New materials and manufacturing techniques are being explored to enhance the performance and capabilities of ceramic resistors.
2. **Potential for Smart Resistors**: The integration of smart technologies into resistors could lead to the development of self-monitoring and adaptive components.
B. Market Trends
The demand for ceramic resistors is expected to grow in emerging technologies.
1. **Demand in Emerging Technologies**: As industries such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and IoT continue to expand, the need for reliable and high-performance ceramic resistors will increase.
2. **Predictions for Future Growth**: Market analysts predict steady growth in the ceramic resistor market, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for electronic devices.
VIII. Conclusion
In summary, ceramic resistors are vital components in modern electronics, offering a range of specifications and advancements that enhance their performance and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, staying updated on the latest specifications and trends in ceramic resistors is essential for engineers and manufacturers. Their role in various applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices, underscores their importance in the ever-changing landscape of technology.
IX. References
For further reading and in-depth research, consider exploring the following resources:
1. Research papers on ceramic resistor technology and advancements.
2. Industry reports on the market trends and future predictions for ceramic resistors.
3. Articles discussing the applications and specifications of ceramic resistors in various fields.
By understanding the latest developments in ceramic resistor technology, professionals can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and reliability of their electronic designs.